Overview
Content encryption is provided by the use of Symmetric Keys. The Portal stores a centralized collection of Secret Keys. Clients obtain access to these keys through common permissions granted upon onboarding. Clients may use these Secret Keys to encrypt and send data to Enterprise Kitchen.
NOTE: encryption and decryption MUST use the same method.
To prevent revealing possible encryption patterns, every HTTP or WebSocket request must contain an Initialization Vector (IV) in the meta data or body of the message. Because both Enterprise Kitchen and the POS have access to the Portal and the Secret Keys—along with the random IV per each request—both are able to decrypt and read the payload.
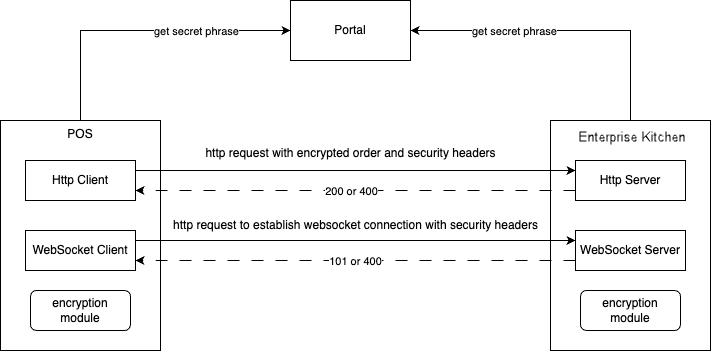
Secret Key Retrieval Process
Enterprise Kitchen and POS system retrieve the Secret Keys from the Portal using a secure HTTPS protocol. Since access is controlled and authenticated the pass phrase is secure.
HTTP Requests
Every HTTP request requires:
A fingerprint of the secret key used to encrypt the current message
An Initialization Vector
An encrypted payload
HTTP Request Examples
Headers
{
accept: "application/json",
sec-iv: <initialization_vector>,
sec-fingerprint: <secret_key_identifier>,
content-length: 1333,
content-type: "application/json",
host: "192.168.0.1:1111",
user-agent: "Xenial/2.2.133 CFNetfork/1494.0.7 Darwin/23.4.0"
}Body
<encrypted_data>
HTTP Request Errors
HTTP Code | Body | Description |
|---|---|---|
400 | { errorCode: 1, message: 'Incorrect security headers' } | Secure communication is configured on the Portal, but the request does not have all of the required fields (authorization, iv, fingerprint). |
400 | { errorCode: 2, message: 'Unable to decrypt payload' } | An error occurred during message decryption. |
WebSocket Connection and Subsequent Requests
WebSocket communication includes:
Establish a connection
Exchange data
Establish Connection
To successfully establish a WebSocket connection, the client sends an HTTP request that includes the Fingerprint and IV header fields—the same requirements as an HTTP request. Simultaneously, the subsequent WebSocket payload request consists of:
message—data encrypted with a defined algorithmiv—the shared initialization vectorfingerprint—the unique identifier of the secret key
Every client, receiving an Enterprise Kitchen WebSocket payload, must use a Secret Key—obtained from the Portal—and a shared IV in order to successfully decrypt the data contained in the message field.
Establish Connection Example
An HTTP request to establish a WebSocket connection:
GET HTTP/1.1
{
Accept: "*/*",
Accept-Encoding: "gzip, deflate",
Accept-Language: "en-GB,en;q=0.9",
Cache-Control: "no-cache",
Connection: "Upgrade",
sec-fingerprint: <secret_key_fingerprint>,
sec-iv: <initialization_vector>,
Host: "10.130.50.79",
Origin: "ionic",
Pragma: "no-cache",
Sec-WebSocket-Extensions: "permessage-deflate",
Sec-WebSocket-Key: "psnNRnMFTV8RwjV86xGa5Q==",
Sec-WebSocket-Version: "13",
Upgrade: "websocket",
User-Agent: "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7)
AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Mobile/15E148"
}Message Example
{
iv: <initialization_vector>,
fingerprint: <secret_key_fingerprint>,
message: <encrypted_data>
}